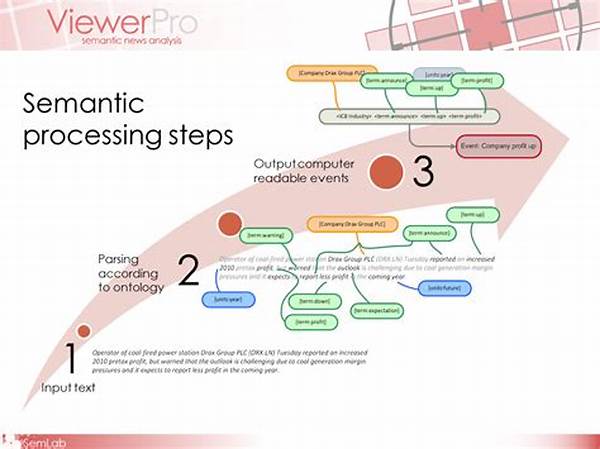
- The Magic Behind Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
- Objectives of Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
- Deep Dive into Semantic Relationships
- Key Actions in Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
- Building a Strong Structure for Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
- Investigating Semantic Relationships
- Illustrations on Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
In the ever-evolving world of technology, the way we understand and interact with text has transformed drastically. From simple keyword searches, we’ve advanced to a point where machines can understand the nuances of human language. Enter semantic analysis in text processing — an essential component of modern-day text interpretation. Imagine, for a moment, a library of vast information, where books don’t just store words but comprehend their meanings, contexts, and implications. That’s what semantic analysis does. It ensures that machines don’t just read text; they understand it. This deep dive into linguistic structures helps in delivering more meaningful and context-aware results, making every application from search engines to chatbots infinitely smarter.
Picture this: you’re searching for “the fastest way to cook pasta,” and you get results about sprinting and marathon techniques. Frustrating, right? Semantic analysis ensures that such blunders are minimized by providing contextually accurate results. With this technology, machines can differentiate between the “barking” of a dog and the “bark” of a tree. This accuracy transforms text processing, making our digital interactions more intuitive and less mechanical. Services that leverage semantic analysis in text processing are not just riding the tech wave; they’re shaping the future by turning simple software into cognitive companions.
From a marketing perspective, semantic analysis empowers businesses to connect with their audience more effectively. Imagine launching a new product tailored precisely to the desires of its target audience, identified through analyzing millions of social media and review comments. Semantic analysis in text processing is the unsung hero of such breakthroughs, providing insights that are gold mines for marketers. It’s not just about understanding words; it’s about understanding your audience’s hearts and minds.
The Magic Behind Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
In a world dominated by vast amounts of text data, businesses need to process and derive meaning from this information efficiently. Semantic analysis in text processing offers a magical opportunity — turning raw data into valuable insights that drive decision-making. But how does this magic actually work?
—
Objectives of Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
What makes semantic analysis in text processing stand head and shoulders above traditional methods? The answer lies in its objectives. This tech marvel isn’t just about parsing text; it’s about understanding the very essence of communication. Let’s embark on this journey, where we decode the secrets and future potential of semantic analysis in text processing.
At its core, semantic analysis seeks to bridge the gap between human language and machine interpretation. The goal is not merely to read or recognize words but to grasp their intents, emotions, and contexts. This involves identifying synonyms, context, and relationships between different pieces of text, making machines more intuitive and accurate in their responses.
For example, a chatbot that excels at semantic analysis won’t just respond to the query “What’s up?” with the usual “I’m a bot!” Instead, it will understand the informal nature of the greeting and engage more naturally. Such interactions are not only technically impressive but also crucial in enhancing user experience, making digital communication more personal and less robotic.
Another significant objective of semantic analysis in text processing is sentiment analysis. By understanding the tone and mood behind written words, businesses can gain invaluable insights into customer satisfaction and perception. Imagine a company navigating through thousands of reviews and instantly understanding overall customer sentiment — a monumental task made simple and effective through semantic analysis.
Deep Dive into Semantic Relationships
Parsing and Understanding Context
Semantic analysis in text processing is not only about understanding individual words but how these words form sentences and convey meaning. Parsing is crucial here, where sentences are broken down, analyzed, and understood. The context is everything, transforming a basic sentence into a meaningful entity.
Beyond parsing, semantic analysis strives to predict and infer meanings that are not explicitly stated. The subtlety of language — especially idiomatic expressions, sarcasm, or cultural references — presents a unique challenge. Yet with advanced algorithms and deep learning techniques, semantic analysis in text processing rises to the challenge, ensuring machines can decode even the most intricate human dialogues.
With these objectives, businesses and developers are better equipped to build systems that are not only precise but are also capable of fostering genuine connections with their users.
—
Key Actions in Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
Building a Strong Structure for Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
Creating an effective framework for semantic analysis in text processing isn’t just technical jargon — it’s the backbone of smart text processing solutions. This structured approach ensures that semantic analysis delivers on its promise of understanding and interpreting human language accurately and efficiently.
The foundation begins with a deep understanding of linguistic rules and patterns. Like a detective, semantic analysis sifts through the information, isolating clues, patterns, and connections. This isn’t a simple dictionary lookup; it’s a blend of linguistic expertise and machine learning that turns chaotic text into organized, meaningful data.
Moving beyond basics, semantic analysis integrates advanced AI models designed to simulate human understanding. These models grow and adapt, learning from their interactions to further enhance their ability to process text. This adaptive capability is a game-changer, enabling systems to evolve with language trends and emerging vocabulary.
Finally, the structure is crowned by seamless integration with diverse applications. From enhancing search engine results to powering intelligent customer service bots, semantic analysis enriches user interactions across various platforms. In this interconnected web of information, the robust structure of semantic analysis ensures clarity, precision, and deeper understanding.
—
Investigating Semantic Relationships
Dissecting Text for Meaning
The heart of semantic analysis in text processing lies in investigating semantic relationships, where the text is dissected for its true intent and meaning. This is not just a scientific process; it’s a fascinating journey into the essence of language.
Imagine a detective unraveling a mystery, piecing together clues to form a coherent narrative. Similarly, semantic analysis in text processing involves dissecting the relationship between words, phrases, and sentences. This isn’t just about detecting the words “cat” and “mat,” but understanding that the “cat sat on the mat.” It’s this nuanced understanding that allows semantic analysis to thrive.
One of the challenges here is understanding implied meanings and cultural nuances. A phrase like “break a leg” isn’t about causing harm, but rather wishing someone good luck. Semantic analysis in text processing has evolved to understand such idiomatic expressions, bridging the gap between rigid machine interpretation and the fluidity of human language.
Beyond simple word relationships, semantic analysis also delves into the emotional and psychological aspects of text. It’s about recognizing sarcasm, joy, disappointment, or even conflict between words. This depth of understanding enables machines to interact more naturally and responsively with humans, opening new frontiers in human-computer interaction.
—
Illustrations on Semantic Analysis in Text Processing
In the grand theater of technology, semantic analysis in text processing takes center stage, transforming the text into interactive and insightful dialogues. Whether it’s powering search engines or enhancing customer service experiences, its impact is profound. As we unfold these illustrations, they serve as a vivid reminder of the dynamism and transformative power of semantic analysis.
Each illustration is a testament to how far we’ve come and how much further we can explore the nexus of language and technology. It’s an invitation to scholars, businesses, and curious minds to delve deeper, innovate, and embrace the boundless potential of semantic analysis in text processing.