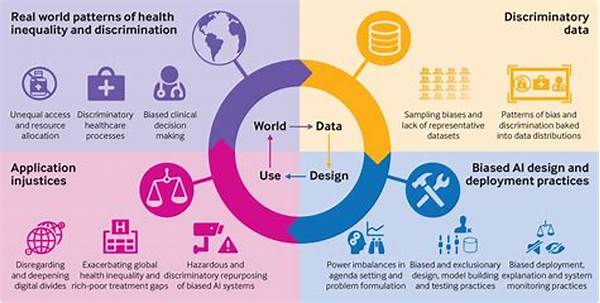
Discrimination Reduction in Algorithms
In today’s fast-paced digital world, algorithms are the backbone of decision-making processes across a multitude of sectors. From recommending products in e-commerce to determining credit scores in finance, these mathematical models influence decisions that affect billions of lives every day. However, as we increasingly rely on algorithms, a pressing issue has emerged: the potential for these systems to exhibit bias, leading to unfair treatment and discrimination. This concern has become a hot topic, attracting attention from researchers, policymakers, and businesses committed to ethical AI practices.
The objective of achieving discrimination reduction in algorithms is not just a technical challenge, but a social imperative. Algorithms, at their core, process historical data to make predictions about the future. Unfortunately, if the data fed into these systems carries the biases prevalent in our society—whether regarding race, gender, or socio-economic status—these biases can be embedded in the algorithm’s logic. The consequences are profound: erroneous predictions can perpetuate inequality, deny opportunities, and erode public trust in AI technologies.
Imagine an algorithm used by a company to shortlist candidates for a job. If this system inadvertently prioritizes male applicants due to historical hiring trends present in the data, it could contribute to gender imbalance within the organization. Similarly, algorithms in the criminal justice system, if biased, might contribute to unfair sentencing, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities. Addressing these challenges is not just about technical fixes; it’s about cultivating a culture of accountability and inclusiveness where technology serves all groups equitably.
Businesses, governments, and communities now demand robust strategies for discrimination reduction in algorithms. This requires a concerted effort to understand the origins of bias and to innovate with solutions that mitigate it. A growing number of tech firms are making strides in this direction, prioritizing ethical considerations alongside technical advancements. From implementing fairness checks to diversifying training datasets, these practitioners are at the forefront of creating AI that upholds principles of justice and equality.
The Challenge of Bias in Machine Learning
Successfully implementing discrimination reduction in algorithms involves a blend of statistical methods, ethical considerations, and collaborative action. But it’s no easy feat. In the following sections, we’ll explore cutting-edge research and real-world applications aimed at minimizing algorithmic bias. Together, these efforts reflect a broader societal shift toward technology that respects civil rights and human dignity, reinforcing the idea that true innovation is ethical innovation.
Discrimination Reduction: An Essential Introduction
In a rapidly digitizing world, the role of algorithms transcends traditional boundaries, influencing a plethora of decisions—some inconspicuous, others life-altering. As artificial intelligence continues its unprecedented expansion into various facets of life, from healthcare to entertainment, the essence of achieving discrimination reduction in algorithms becomes increasingly paramount. This isn’t just an academic concern or an ethical dilemma; it is, in fact, a new frontier of justice and equality in an AI-driven era.
The journey toward discrimination reduction in algorithms is akin to navigating a labyrinth of historical biases embedded deeply in societal data. Consider this: every decision, every judgment call that an algorithm makes is based on historical data fed into it. Alas, if this data carries age-old prejudices—be it racial, gender-based, or socio-economic—these biases can mysteriously emerge as logical outputs of the algorithm. As a result, entire populations can suffer from misjudged decisions, highlighting the urgent need for equitable AI systems.
Imagine living in a world where your score for a loan or your eligibility for a program is tainted by biases, not by your financial health or merit. Picture this in the realm of law enforcement, where algorithms mistakenly flag individuals for higher surveillance based on flawed data patterns. Such scenarios not only sound alarms but spotlight the inconsistency of relying solely on AI without robust mechanisms for discrimination reduction.
Unveiling the Importance of Ethical AI
With the ever-growing influence of AI comes the vital necessity to bridge the gap between technological prowess and ethical responsibility. Enter the concept of discrimination reduction in algorithms—a paradigm dedicated to ensuring that all algorithmic decisions mirror fairness, accuracy, and impartiality. This emerging field is proving to be a lucrative territory not just for tech giants but for startups and ethical consultants who endeavor to make AI systems fail-safe and fair.
The Interplay of Human and Machine Intelligence
While the tech world buzzes with excitement over advanced machine learning techniques, the stark reality is that human oversight remains indispensable. Algorithms must include checks and balances, where diverse teams evaluate and amend AI outputs to align with societal values. This collaborative approach signifies a path where we harness AI’s power while safeguarding the principles of fairness and inclusivity.
In the effort towards discrimination reduction in algorithms, the narrative spans scientific innovation, ethical introspection, and practical adaptability. As pioneers in this saga decode the complexities, they lay the groundwork for a future where AI systems are not just smart but are profoundly compassionate and just.
Summary Insights
Embracing Fair Algorithms
We are at an exciting juncture where technology and ethics intersect, pledging a harmonious collaboration for a fairer tomorrow. As the quest for discrimination reduction in algorithms advances, tech innovators and ethical thinkers unite to navigate this brave new world. What lies ahead is a commitment to refine AI systems—ensuring they prepare us for a truly inclusive future.
Understanding the nuances of bias detection and mitigation involves continuous learning, scrutinizing new developments, and frequently testing AI solutions for fairness and transparency. Only then can we confidently rely on these digital systems to uphold and mirror values intrinsic to human dignity.
The Path Forward: Tools and Techniques
By integrating diverse datasets, leveraging advanced statistical methods, and fostering transparency in AI systems, discrimination reduction in algorithms is attainable. It requires ardent dedication from all tech stakeholders—from coders to CEOs, from policy advisors to end-users. The mission is clear: to continually refine and optimize AI technologies so that they serve humanity justly.
As we wrap our heads around the continued evolution of discrimination reduction in algorithms, this narrative morphs into a testament of resilience, a roadmap of ethical innovation, and an emblem of societal progression. The countdown is on for crafting an algorithmic future where technology is not just adept, but genuinely equitable and humane.