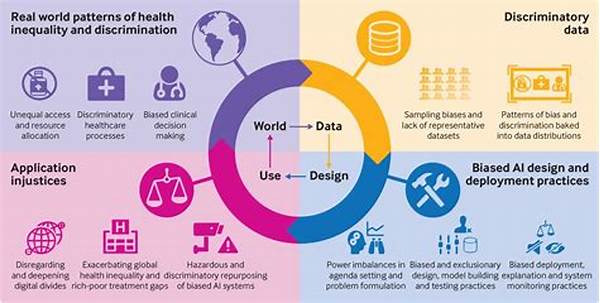
Artificial intelligence (AI) is undoubtedly altering various facets of our daily lives, from how we access information to how we make decisions. Yet, for all its potential, there exists a shadowy side that often goes unnoticed: AI bias. Reducing this bias doesn’t just rectify algorithmic inequities. It profoundly impacts society as a whole. But how? Imagine decision-making processes that are fair, equitable, and reflective of an unbiased truth. This is the promise AI bias reduction holds for society. This article delves into the societal impacts of AI bias reduction and why it matters more than ever.
In an era where AI influences financial services, healthcare, employment, and even criminal justice systems, the societal impacts of AI bias reduction are too significant to ignore. By addressing biases ingrained within AI systems, we commence a journey toward fairness and inclusivity in society. AI models often reflect historical data; so, if biases exist within that data, AI systems perpetuate them at scale. Elimination of this bias creates a leveled playing field where decisions are a true representation of merit and need. For instance, unbiased AI could mean equal loan approvals regardless of one’s race or gender, fostering economic growth and financial inclusion.
Consider the health sector, where the societal impacts of AI bias reduction can sometimes be a matter of life or death. AI-driven diagnostics and treatment plans promise to revolutionize patient care, but biased algorithms might misdiagnose or inadequately treat patients from specific ethnic backgrounds. Bias-free AI, therefore, enhances healthcare equality, ensuring everyone receives accurate and effective treatment and prolonging lives in the process.
Ultimately, addressing AI bias aligns with a broader societal push toward justice and equality. The societal impacts of AI bias reduction extend to institutions and cultures themselves. By challenging AI systems to shed bias, we also challenge societal norms that have long gone unquestioned. The potential ripple effect is massive, laying the groundwork for a more inclusive future. Far from just technical upgrades, these changes are about remodeling society for the better.
The Roadmap to Bias-Free AI
Achieving bias-free AI is easier said than done. It requires collaboration among technologists, ethicists, and policymakers to establish new guidelines and refine existing algorithms. This isn’t merely an IT problem, but one that demands a concerted societal effort. Are we ready to make it?
Creating a society where AI systems are fair, inclusive, and accurate demands understanding both the complexities and the strategies for reducing bias in these intermediaries.
The key phrase “societal impacts of AI bias reduction” implies a layered approach, blending technology and humanity. Addressing AI bias requires acknowledging its origins, often in historical data and systemic biases that have shaped our societies. Therefore, the first step involves identifying these biases. Researchers have found that automated systems trained on flawed data reflect those same biases, underscoring the importance of integrating diverse datasets from the beginning.
Moreover, embracing explainable AI can help demystify algorithms, making it easier to detect inherent biases. Holding AI systems accountable involves not just transparency, but also the utilization of auditing mechanisms to ensure ongoing fairness. This ongoing process involves not just technologists but stakeholders from all sectors of society, ensuring a communal approach in fine-tuning AI systems that impact our daily lives.
Collaboration and Continuous Learning
It’s vital, then, that AI developments aren’t siloed. The societal impacts of AI bias reduction are magnified when tech firms, academia, and policymakers work in tandem. This collaboration fosters continuous learning, essential for methodologies that can keep pace with evolving societal norms and technological advances.
Examples of Societal Impacts of AI Bias Reduction
Addressing AI bias, therefore, is not just another buzzword—it’s a necessity for a modern and equitable society. Let’s continue to push for greater transparency, collaboration, and diligence as we march towards an AI-integrated future.
The Real Life Impact of Reducing AI Bias
AI bias might sound like a futuristic problem, but it has tangible impacts today, affecting critical sectors from banking to law. Reducing this bias doesn’t just have hypothetical benefits—it can genuinely transform lives.
For instance, in the arena of employment, biased AI might inadvertently screen out qualified candidates from minority backgrounds due to subtle biases in historical hiring data. Correcting this could unlock a more diverse workforce, driving innovation and economic performance on a broader scale. Similarly, in banking, bias reduction can facilitate more accessible loans for traditionally underrepresented demographics, promoting financial inclusion and, in turn, gradually closing the wealth gap.
The societal impacts of AI bias reduction are not just theoretical constructs unfurled in research papers. They make daily headlines, with stories of AI misjudgment affecting real lives. By reducing AI biases, we not only improve system efficacy but also foster a society more aligned with values of equity and inclusive progress.
Tackling Resistance and Building Trust
Yet, reducing AI bias is not without its challenges. Resistance to change and skepticism about automated decision-making must be managed with care. Building trust in AI systems involves demystifying the technology for the public and ensuring transparency in AI processes. Only then can the societal impacts of AI bias reduction truly be realized, cultivating an environment where human potential is not sidelined but enhanced.
By charting a course towards AI devoid of bias, we pave the way for a more just society, one algorithm at a time. This commitment transcends technology, becoming an ethical obligation to future generations, ensuring societal impacts that resonate far beyond market trends and technological milestones.
Benefits of Reducing AI Bias
In summary, the societal impacts of AI bias reduction serve as a powerful catalyst for change, heralding a future where tools serve as bridges rather than barriers. Imagine banking systems that approve loans based purely on financial history, educational algorithms that tailor learning experiences without cultural prejudice, or judicial AI systems that assess cases without inherited biases. These are not mere fantasies; they are achievable realities with the commitment to reducing AI bias. Technology evolves, and with it, we have the responsibility and potential to evolve society—fairer, more inclusive, and poised for progress in the AI era.